Fennel seeds are the dried fruits of the plant Foeniculum vulgare and are commonly used as a spice in many cuisines. Their gentle sweetness and refreshing aroma have made them a popular kitchen ingredient for generations. Beyond their flavor, fennel seeds naturally contain several plant compounds that give them their distinctive qualities.
Naturally Occurring Aromatic Oils
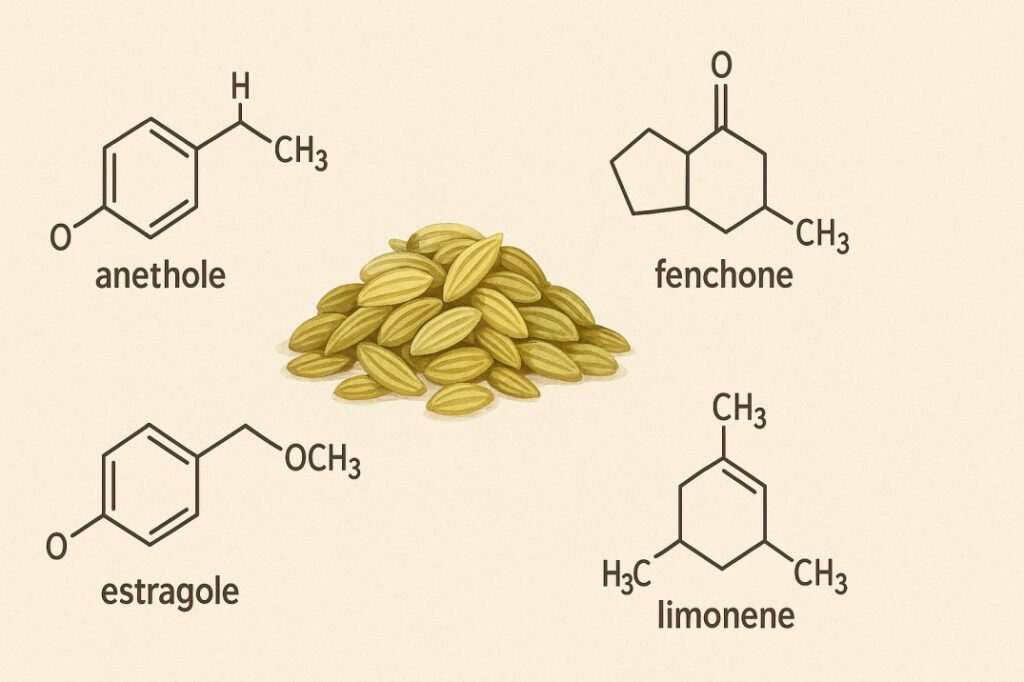
One of the key compounds found in fennel seeds is anethole, which is responsible for their mild, licorice-like taste. Alongside anethole, natural oils such as fenchone and estragole add to the seed’s fresh and slightly warming scent. These aromatic oils are what make fennel seeds especially popular in teas, spice mixes, and after-meal blends.
Antioxidant Plant Compounds
Fennel seeds also contain naturally occurring antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic compounds. These substances are present in many plant-based foods and contribute to fennel seeds’ role as a traditional, wholesome ingredient in everyday diets.
Source of Dietary Fiber
In addition to their aromatic compounds, fennel seeds provide small amounts of dietary fiber. Fiber is a natural component of many seeds and helps support balanced eating when included as part of a varied diet.
Final Thoughts
The combination of aromatic oils, plant antioxidants, and fiber gives fennel seeds their lasting appeal. When used in normal culinary amounts, they remain a simple and natural addition to meals, offering flavor and tradition in one small seed.
Source:
National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) – Foeniculum vulgare overview